
Mathematik-Online lexicon:
|
[home] [lexicon] [problems] [tests] [courses] [auxiliaries] [notes] [staff] |

|
|
Mathematik-Online lexicon: | ||
Multiple Integral | ||
| A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z | overview |
![\includegraphics[width=0.6\linewidth]{bsp_integral1}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel543/img3.png)
Using a square grid with grid-width ![]() leads to the Riemann sum
leads to the Riemann sum
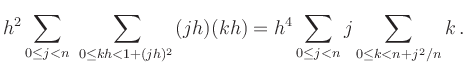

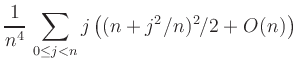 |
|||
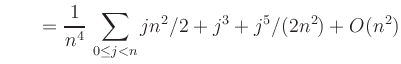 |
|||
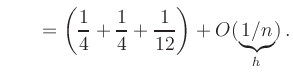 |
see also:
| automatisch erstellt am 22. 9. 2016 |