
Mathematics-Online course: Linear Algebra - Basic Structures - Bases
|
[home] [lexicon] [problems] [tests] [courses] [auxiliaries] [notes] [staff] |

|
|
Mathematics-Online course: Linear Algebra - Basic Structures - Bases | ||
Orthogonal Projection | ||
| [previous page] [next page] | [table of contents][page overview] |
![\includegraphics[width=0.6\linewidth]{a_orthogonale_projektion}](/inhalt/aussage/aussage528/img4.png)
If
![]() is a orthogonal basis
of
is a orthogonal basis
of ![]() , then we have
, then we have
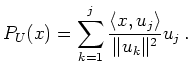
| automatically generated 4/21/2005 |